GOOGLE FIXES FIRST ACTIVELY EXPLOITED CHROME ZERO-DAY OF 2024
📗 Date: 17 Jan, 2024
Source: Beeping Computer

Citrix urged customers on Tuesday to immediately patch Netscaler ADC and Gateway appliances exposed online against two actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities.
The two zero-days (tracked as CVE-2023-6548 and CVE-2023-6549) impact the Netscaler management interface and expose unpatched Netscaler instances to remote code execution and denial-of-service attacks, respectively.
However, to gain code execution, attackers must be logged in to low-privilege accounts on the targeted instance and need access to NSIP, CLIP, or SNIP with management interface access.
Also, the appliances must be configured as a gateway (VPN virtual server, ICA Proxy, CVPN, RDP Proxy) or an AAA virtual server to be vulnerable to DoS attacks.
The company says that only customer-managed NetScaler appliances are impacted by the zero-days, while Citrix-managed cloud services or Citrix-managed Adaptive Authentication are not affected.
The list of Netscaler product versions affected by these two zero-day vulnerabilities includes the following:
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 14.1 before 14.1-12.35
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.1 before 13.1-51.15
- NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway 13.0 before 13.0-92.21
- NetScaler ADC 13.1-FIPS before 13.1-37.176
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-FIPS before 12.1-55.302
- NetScaler ADC 12.1-NDcPP before 12.1-55.302
According to data provided by threat monitoring platform Shadowserver, just over 1,500 Netscaler management interfaces are now exposed on the Internet.
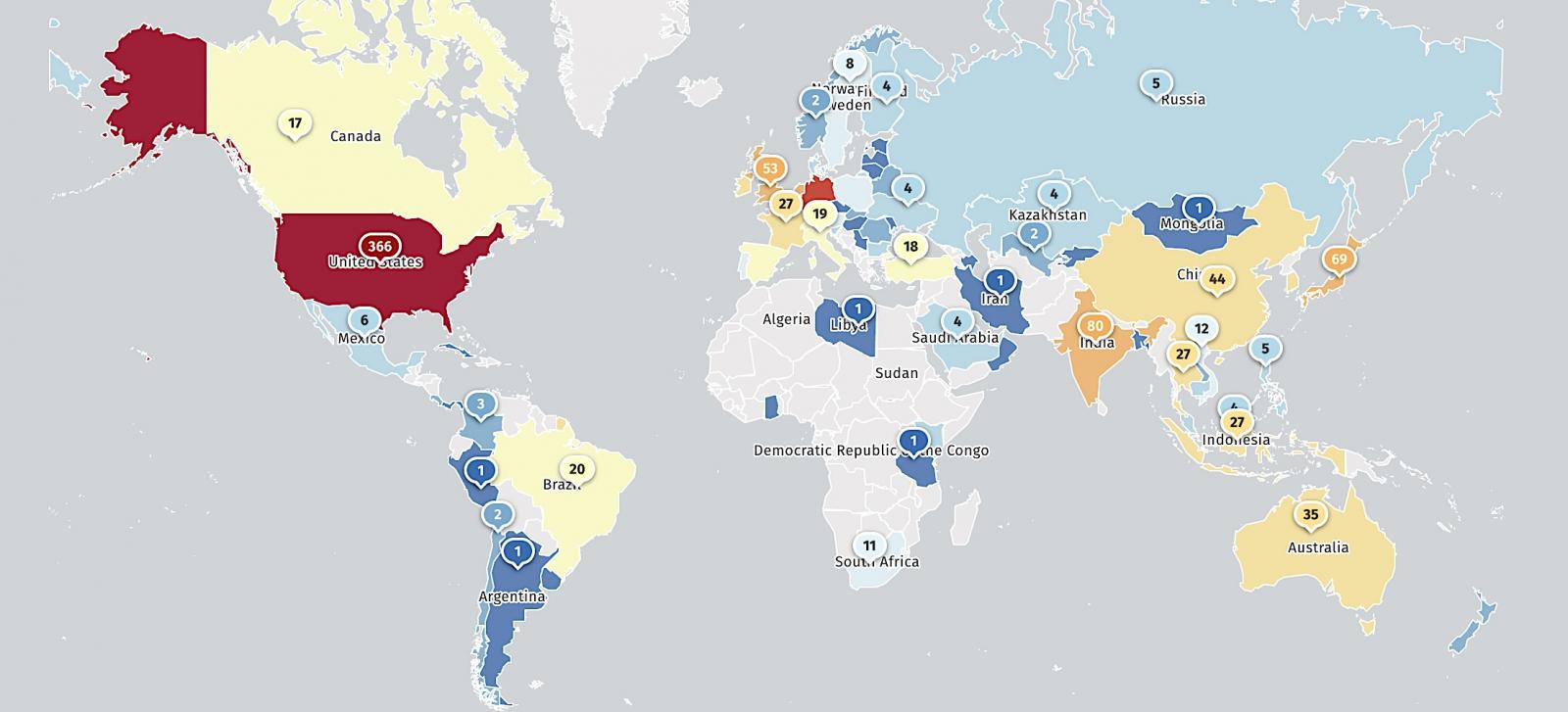 Netscaler management interfaces exposed online (Shadowserver)
Netscaler management interfaces exposed online (Shadowserver)
In a security advisory published today, Citrix urged all admins to immediately patch their Netscaler appliances against the two zero-days to block potential attacks.
“Exploits of these CVEs on unmitigated appliances have been observed,” the company warned. “Cloud Software Group strongly urges affected customers of NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway to install the relevant updated versions as soon as possible.”
Those still using NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway version 12.1 end-of-life (EOL) software were also advised to upgrade them to a version still under support.
Admins who cannot immediately deploy today’s security updates should block network traffic to affected instances and ensure they’re not exposed online.
“Cloud Software Group strongly recommends that network traffic to the appliance’s management interface is separated, either physically or logically, from normal network traffic,” Citrix said.
“In addition, we recommend that you do not expose the management interface to the internet, as explained in the secure deployment guide. Removing such exposure to the internet greatly reduces the risk of exploitation of this issue.”
Another critical Netscaler flaw patched in October and tracked as CVE-2023-4966 (later dubbed Citrix Bleed) was also exploited as a zero-day since August by various threat groups to hack into the networks of government organizations and high-profile tech companies worldwide, such as Boeing.
HHS’ security team, the Health Sector Cybersecurity Coordination Center (HC3), also issued a sector-wide alert urging health organizations to secure their NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway instances against surging ransomware attacks.